How to choose the right printer in 5 easy steps


CHOOSING THE RIGHT PRINTER IN 5 EASY STEPS
Barcode systems are used in every commercial activity and in every corner of the world.
Which markets and industries use barcodes all the time?
Transport, logistics, pharmaceutical companies, shipping
Distribution & dispensing stations, industrial production
After researching the market, you will decide on the printer that suits your working environment & combined with the barcode label that suits your needs, you will get the maximum results, in terms of ergonomics and productivity.
Choose the printer you need in 5 steps - criteria.
Step 1. Determine the print volume
How many labels will your company print per day, week and month?
Predicting print volume is an important parameter that drives you to specific printer categories. Your choices by category based on the print volume parameter are as follows:
1. PORTABLE BARCODE PRINTERS
Designed for demanding printing conditions. They are usually printed on the move and are chosen when accuracy and speed are the main performance criteria.In this category there are:
Portable barcode label printers. These are used to print barcode labels, receipts and tickets.They are ideal for:
- retail
- Hosting
- Supply Chain
- Warehouses
- retail and healthcare
- & picking stations
View : Portable barcode printers
The portable barcode receipt printers. They are used for printing receipts, orders, etc. They are ideal for:
- direct sale of products
- direct sales of goods
- sales
- in-store check-out
- e-citation applications
View: portable barcode receipt printers
2. DESKTOP BARCODE PRINTERS
Designed for low volume label printing of 2 rolls (1000 labels per day), desktop barcode printers are ideal for:
- Offices
- retail
- Retail - Retail stores - Healthcare
- Healthcare Retailers, Healthcare Retailers, Healthcare Retailers - Small & Medium Businesses
- Packaging and transport
- light manufacturing
- small and medium warehouse management
View: desktop barcode printers
3.MID-RANGE BARCODE PRINTERS
Reliable and robust, these printers are designed for medium to high volume printing in the range of 2000-7000 labels/day:
- Sorting & picking stations
- Warehouse management
- Product tracking & tracing
- Manufacturing
- logistics
- Healthcare environments
4.HIGH PERFORMANCE BARCODE PRINTERS (industrial)
Designed for continuous operation and critical production applications. High volume printing requirements: 5000 - 10000 labels per day. industrial barcode printers are ideal for:
- Warehouses
- Product sorting & collection stations
- product traceability
- production
- transport
- logistics
- Healthcare environments.
Step 2. Determine how the barcode label itself will be used.
Choosing the right label starts with evaluating the following criteria:
How will I use the barcode label? What environment will the label be in?
Barcode label selection parameters.
- What surface will it be applied to?
- Ambient temperature (max-min)
- Shelf life
- Use of chemicals or not
The following parameters will guide you to a label type suitable for your application.
a. SURFACE
Depending on the surface, the paste will also be affected. The surface will therefore determine the type of adhesive and label stock you need. Labels generally adhere best to a clean, smooth, non-porous surface. If, for example, the surface is rough and not clean, you will need a permanent/strong label adhesive:
- Shape: flat, angled or curved
- Composition: glass, metal, plastic, paper, wood, fabric, polycarbonate
- Texture: rough, smooth, porous, non-porous
- Purity: dirty, greasy, frozen, dusty
b. TEMPRATURE
When evaluating temperature, you should consider both the application temperature and the expected temperature during use. Will the label have to withstand a refrigerated environment? Or high temperatures? Will it be used before or after a product is frozen? Temperatures above 930C or below -53C require thermal transfer labels.
c.CHEMICAL USE
Consider whether the label will be exposed to chemicals such as detergents, oils, grease or alcohol. For example, a label exposed to heavy or medium chemicals such as oil/acetone will require a thermal transfer label with an ultra-strong resin ink film to prevent degradation.
d.EXTERIOR/INTERIOR
The environmental conditions will determine the type of adhesive required and the durability of the print. If the label will be in an outdoor environment, you will need to determine factors such as: rain, sun, humidity, extreme heat & cold. If indoors, determine factors such as lighting (UV, fluorescent) & environment (freezer, warehouse, retail space).
e. STANDARDS COMPLIANCE REQUIREMENTS
It is important to know if the label for the product or service you are marketing must meet certain requirements in order to comply with a standard. Examples of standards include: UL, CSA, RoHS, REACH, MIL-SPEC and SAE.
f. LIFETIME
At this point you need to consider the life cycle of your product. The life cycle is divided into 2 intervals. Interval 1. The longest period of time from the time it is manufactured to the time it is no longer fit for use/sale. Interval 2. The shortest period of time from the moment the product is sold, stored until the moment it is finally consumed/used.
g. LABEL SIZE - DIMENSIONS
What will it be used for? Will it be used as a patient wristband, clothing tag, in a container or as a transport label? The size of the label determines the size of the print head and the dpi (dots per inch). Large labels require standard resolution print heads, while small labels require a higher resolution print head (dpi) to be legible.
i. INDUSTRY - ACTIVITY SECTOR
There are industries that require the production of labels that comply with regulations and standards, or labels that require high accuracy and printing with no margin for error.It is essential that you understand the requirements of your industry and that you comply with the regulations and restrictions that govern the market in which you operate.Choosing the wrong label can result in low rates of accurate barcode reading due to label tampering.
View the available dimensions here: Label dimensions

Step 3. Review the various printing technologies.
Essentially, you have to match the printing technology to your needs.
LASER PRINTERSLaser printing capabilities: high quality text and graphics on paper labels. Barcode print density is high and can be easily read by infrared scanners. Laser barcode printers are not suitable for industrial use. They cannot produce water and chemical resistant labels.
INKJET PRINTERS
Inkjet printer capabilities: typically used for high speed production applications where barcodes need to be placed at high speed. Inkjet printers can be expensive and complicated to use. This class of printer requires constant monitoring and control to prevent jamming and maintain print quality. They cannot print barcodes on a dark background as the ink will clog and be difficult to read. When choosing an inkjet printer, choose a model that is designed to print barcodes.
Thermal Transfer or direct thermal printers
Both thermal transfer and direct thermal printers use a thermal print head to print onto a blank label. Generally speaking, thermal printers are an ideal solution for printing text, images, graphics & barcodes because they have high accuracy in printing and give a consistent, consistent quality combined with high speed.Printers that are only direct thermal cannot be thermal transfer (use ink ribbon) Printers that are thermal transfer can also print with direct thermal (without using ink ribbon)
DIRECT THERMAL PRINTERS
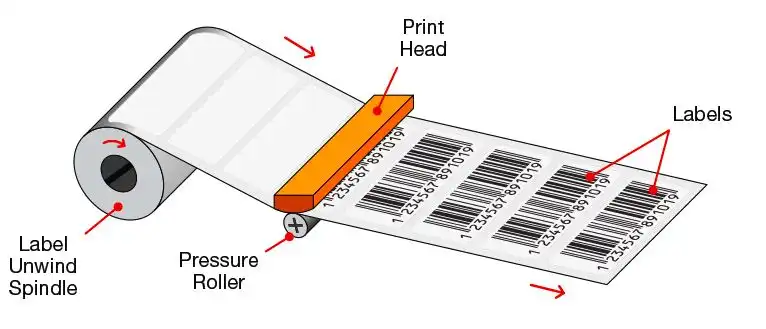
In direct thermal printers, the print head comes into direct contact with the label material, which acts on the coating to produce the print. High reliability/high durability with very few moving parts, minimising the need for maintenance and repair. A label printed with a direct thermal printer is sensitive to light, heat and abuse and has a shorter life than a label printed with a ribbon (thermal transfer); for example, if such a label is used on a pallet and exposed, the surface of the paper will blacken, rendering the barcode useless.
Ideal for:
- Transport labels
- Patient - visitor identification
- receipts
- Food & Drink
- Tickets
Thermal printers that are direct thermal only (no ribbon) have lower costs because they do not contain the hardware necessary to drive and control the ribbon during printing; without ribbon and ribbon usage parts, the printer has fewer components to break or wear out, resulting in lower repair/maintenance costs.
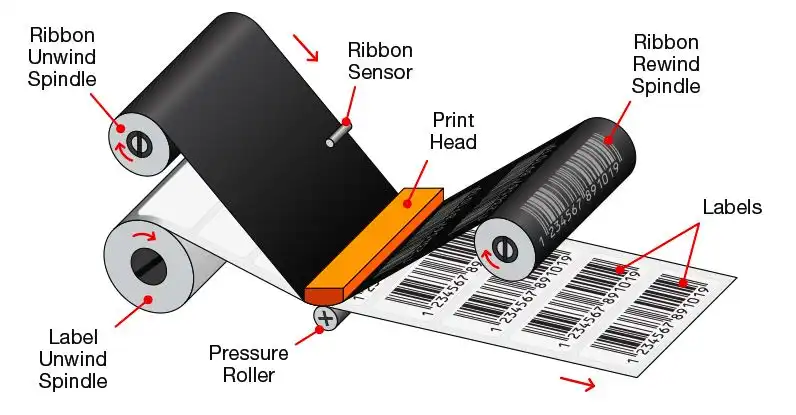
THERMAL TRANSFER PRINTERS
In thermal transfer printers, the print head applies heat to the ribbon to print. The ribbon is made of wax or resin that is absorbed into the surface of the label. Ideal for barcode printing where accuracy is paramount. Unlike direct thermal printers, thermal transfer printers accept a wider range of label roll materials such as paper, polyester and polypropylene. The ribbon and label must be carefully selected to ensure print performance and durability.
There is a much wider variety and combination of label materials and adhesives. In this category it is possible to produce labels that can withstand extreme temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, chemicals, etc.
For example, pharmaceutical or chemical products are ideal candidates for thermal transfer labels. The cost is comparatively higher, but the readability and durability of the label is significantly higher.

Step 4. Identify your connectivity needs.
Below are examples of connectivity that printers typically have by category
Portable barcode label printers.
Portable receipt printers: Mobile receipt printers. USB 2.0, Serial (RS233), Bluetooth, Wireless 802.11b/g, Bluetooth, iRDA.
Desktop Barcode Printers: USB 2.0, USB Host 2.0, Ethernet LAN (10/100), Serial (RS233), Parallel, Wireless 802.11b/g/n, Bluetooth.
Mid-range barcode printers: USB 2.0, USB Host 2.0, Ethernet LAN (10/100), Serial (RS233), Parallel, Wireless 802.11b/g, Bluetooth, Industrial Interface, SDIO, GPIO.
High performance barcode printer - ( industrial): USB 2.0, USB Host 2.0, Ethernet LAN (10/100), Serial (RS233), Dual Serial (RS232), Parallel, Wireless 802.11b/g, Bluetooth, Industrial Interface, SDIO, GPIO.
Step 5. Research the latest market models and new technologies being used in your industry.
As with all technologies, professional barcode printing has come a long way.
Spend time researching the latest models in the category you are interested in, and understand what improvements they have incorporated that can really benefit your business.